Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

The overall objective of the ESPOIRS project is to obtain a better understanding of the variability, statistical properties and formation mechanisms of intense tropical precipitation at regional and local scales. ESPOIRS is thus interested in the entire life cycle of precipitation at several space-time scales. * Through the analysis of the distribution of the large-scale humidity field which drives the formation of precipitation at the regional scale using a GNSS network. * Through the characterization of internal (dynamics, microphysics) and external (interactions with the relief) processes, which drive the formation and life cycle of extreme weather events at the local scale => transportable Polarized Doppler X-band precipitation radar.
-

The ressource describes the dataset obtained by deploying the GAMIC GMWR-25-DP RADAR in the South of Reunion Island, in Saint Joseph.
-

WW3 model reanalysis on SWIO (south-western indian ocean) area at 0.5 degree of resolution
-
.png)
Le radar BASTA est un radar nuage (95GHz) dédié à l’étude des nuages et du brouillard. Le radar mesure l’énergie rétrodiffusée par les hydrométéores, cette énergie peut donc être reliée à la quantité d’eau contenue dans le nuage (liquide et glace). Il fonctionne en routine quotidiennement sur le site de l’observatoire du Maïdo, sur l'Ile de La Réunion. Le radar BASTA Réunion a été calibré au LATMOS avant son installation à la Réunion. Ce jeu de données est au format niveau L0. Paramètre principal: Profil vertical de réflectivité radar, mesure du décalage Doppler. Contexte de la mesure: observation routine.
-
Honga Tonga Aerosols measurments from lidars at Maïdo observatory, Reunion Island (21.08°S, 55.38°E)
To do
-
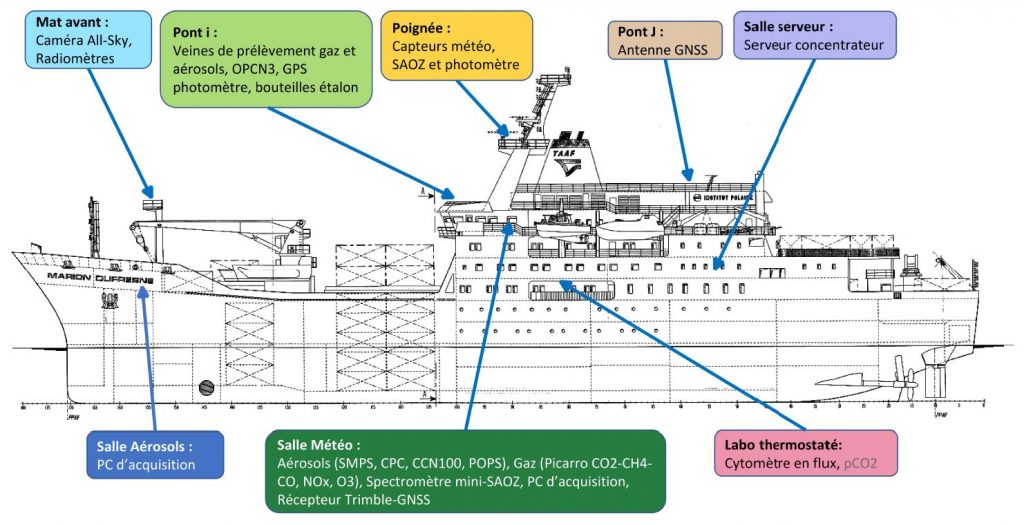
Le projet MAP-IO vise à effectuer des observations atmosphériques et de biologie marine sur le long terme dans la région de l’ouest de l’océan Indien. Ces données seront bancarisées en open-source à la fois dans les réseaux internationaux (ICOS, ACTRIS) qui sont utilisés pour initialiser et valider les modèles climatiques du GIEC et les satelittes et sur la base de données GeOSUR dédiée à la recherche et à l’ensemble des acteurs du territoire. Elles permettront d’avancer sur notre compréhension des échanges océan-atmosphère, sur la pollution régionale et sur les mécanismes chimiques en permettant d’améliorer et d’adapter les paramétrisations utilisées dans les modèles numériques de prévision du temps et de climat sur la région ouest de l’océan Indien. La stratégie de MAP-IO s’inscrit dans la continuité et la valorisation des investissements de la région Réunion en renforçant les bases de données des programmes scientifiques ReNovRisk Cyclones et Changement Climatique (INTERREG V) et UV-INDIEN (INTERREG V) et l’infrastructure « Observatoire du Maïdo » (FEDER). MAP-IO viendra renforcer la place de la Réunion dans les grandes infrastructures de recherches Européenne ACTRIS (http://www.actris.fr/) et ICOS (https://www.icos-france.fr/). A terme, l’objectif est de faire de La Réunion un hub de surveillance du climat et des changements globaux de niveau international permettant une percolation des produits de recherche vers l’activité économique et sociétal du territoire. MAP-IO s’inscrit également dans une action forte de La Réunion pour la croissance bleue dans les DOM (livre bleu de l’outre-mer, 2018). MAP-IO se positionne dès à présent dans les lignes directrices de la mission 3 du programme Horizon Europe (2021-2027) « Santé des océans et des eaux naturelles » et au sein des partenariats institutionnels du domaine 3 « Leadership européen dans le domaine de la métrologie, y compris un système intégré de métrologie ». Ce positionnement ouvrira des nouvelles opportunités de réponses des scientifiques de La Réunion aux appels d’offres au programme européen pour la recherche et l'innovation (Horizon Europe). Questions de recherche L’objectif du projet MAP-IO est d’étudier la composition de l’atmosphère et les processus océan-atmosphère ayant un impact sur le climat régional et la prévision numérique du temps. Ce programme scientifique s’appuie sur la bancarisation de données océaniques et atmosphériques en équipant le navire Marion Dufresne de plusieurs systèmes de mesure de l’atmosphère pérennes et autonomes. Ces systèmes d’observations ont cinq buts principaux: - Documenter l’état de surface océanique et la composition biologique en phytoplancton ; données permettant de participer à la calibration des données satellites et à la validation des modèles océaniques et biologiques sur l’océan Indien et austral. - Surveiller les changements atmosphériques globaux en particulier dans la région de l’océan Indien très faiblement documentée (réseaux NDACC, ACTRIS, ICOS). Bancariser les données en open data. - Étudier les transports de masses d’air et la redistribution des aérosols et des composés chimiques dans la troposphère et la stratosphère (programmes IGAC et SPARC). - Documenter les émissions de gaz et d’aérosols marins pour les modèles atmosphériques de prévision numérique ou de climat (programme SOLAS). - Renforcer les réseaux régionaux d’observation du changement climatique régional déployés dans le cadre des programmes ReNovRisk Cyclones et Changement Climatique (INTERREG-V), IOGA4MET (TAAF, AAP Iles Eparses) et UV-indien (INTERREG-V). Actions et méthodes scientifiques Le programme MAP-IO s’est construit autour de deux fiches actions. La fiche action 1 « amélioration de la connaissance » correspond aux études scientifiques qui seront abordées à partir des observations à bord du Marion Dufresne pendant 24 mois. Elle sont déclinés en 5 sous actions. - 1.1 : Distribution spatiale et hétérogénéité structurelle des groupes fonctionnels du phytoplancton et du microzooplancton, couplage avec les images satellite de couleur de l’eau. Mise en œuvre d’un cytomètre en flux. - 1.2 : Échanges océan-atmosphère: aérosols marins et composition de la couche limite marine. Mise en œuvre de mesures in-situ de gaz et d’aérosols. - 1.3 : Climatologie et variabilité des rayonnements UV et de l’ozone dans l’Océan Indien. Mise en œuvre de mesures UV A,B et C et de colonne intégrée d’ozone. - 1.4 : Étude des panaches d’aérosols issus des feux de biomasse et en provenance du Sud de l’Afrique, de l’Amérique du Sud et de l’Asie du Sud-Est. Mise en œuvre d’un photomètre solaire/lunaire pour l’épaisseur optique des aérosols. - 1.5 : Surveillance du champ de vapeur d’eau à l’échelle du bassin SOOI. Mise en œuvre d’un GNSS. La fiche action 2 correspond au management et à la valorisation du programme. Cette action intègre la (i) coordination et la gestion administrative et financière du programme et (ii) une conférence de restitution du programme et d’organisation d’un modèle économique de fonctionnement perenne de MAP-IO. Partenaires MAP-IO intègre une équipe de 17 scientifiques de haut niveau, responsables notamment de plusieurs services nationaux d’observation de l’atmosphère tels que NDACC, CLAP et PHOTON et bien intégrés au sein des infrastructures de recherche Européenne ACTRIS et ICOS. Dans ce cadre MAP-IO permettra de renforcer les liens collaboratifs entre scientifiques issus de 7 laboratoires de métropole et ceux de l’université de La Réunion. Ce réseau de scientifique pourra se densifier si l’université de La Réunion et ses partenaires au travers de MAP-IO montrent leur capacité à maintenir sur le long terme ces observations régulières uniques au monde.
-

The resource provides two land cover maps of Réunion Island for the years 1950 and 2022 derived from the analysis of ortho-photographs at the island scale (Source IGN). The produced typology uses five cover classes: forest, low vegetation, agriculture, urban, and shadow (related to topography). The method used is based on encoding the two aligned rasters, converted into a single band of grayscale for 2022, using a vision-transformer deep learning model. From the features calculated for each pixel, a random forest classification model is trained separately for each year using a set of ROIs (Regions Of Interest), target polygons delineated within each of the selected classes through photo-interpretation of the original images. Model validation is performed on independent sets of polygons also defined by photo-interpretation. The maps provided in the resource are derived from the prediction of cover classes for both years using the trained and validated models. These are raw predictions, meaning that no post-processing has been applied to reduce potential noise due to classification errors. The shared resource is part of the results from the FRAG'ILE research and development program (FRAGmentation en milieu InsuLairRE, UR / CBNM/ IRD, funded by OFB, https://fragile.frama.io).
-

Le radar mini-BASTA est un radar nuage (95GHz) dédié à l’étude des nuages et du brouillard. Le radar mesure l’énergie rétrodiffusée par les hydrométéores, cette énergie peut donc être reliée à la quantité d’eau contenue dans le nuage (liquide et glace). Il fonctionne en routine quotidiennement sur le site de l’observatoire du Maïdo, sur l'Ile de La Réunion. Ce jeu de données est au niveau L0, et les données sont non calibrées. Paramètre principal: Profil vertical de réflectivité radar, mesure du décalage Doppler. Contexte de la mesure: observation routine.
-

This ressource is part of the action 1 of the ESPOIRS Project. Multiple GNSS Stations have been installed or updated in the SWIO and the data are available here. "TO ADD : Different datasets, list of stations, etc ...."
-

Weekly and monthly physico-chemical water samples of "Rivière des Pluies" watershed, Reunion Island
 Geosur
Geosur